How To Sum A Variable By Group In Network Data R
This article explains how to use a type of role chosen an aggregate office to sum the data in a query result set up. This commodity besides briefly explains how to use other aggregate functions, such as COUNT and AVG to count or average the values in a result fix. In addition, this article explains how to use the Full Row, a feature in Access that y'all utilise to sum data without having to alter the blueprint of your queries.
What exercise you want to do?
-
Understand means to sum data
-
Fix some sample data
-
Sum data past using a Total row
-
Calculate one thousand totals past using a query
-
Calculate grouping totals past using a totals query
-
Sum information across multiple groups by using a crosstab query
-
Aggregate office reference
Sympathize ways to sum data
You tin can sum a column of numbers in a query by using a type of part called an aggregate function. Aggregate functions perform a calculation on a column of information and render a single value. Access provides a diverseness of amass functions, including Sum, Count, Avg (for computing averages), Min and Max. You sum data by calculation the Sum function to your query, you count data by using the Count function, and and so on.
In add-on, Access provides several ways to add Sum and other amass functions to a query. You lot tin can:
-
Open your query in Datasheet view and add a Total row. The Full Row, a feature in Admission, allows you to use an aggregate function in one or more columns of a query event set without having to change the design of your query.
-
Create a totals query. A totals query calculates subtotals across groups of records; a Total row calculates yard totals for i or more columns (fields) of information. For example, if y'all want to subtotal all sales by urban center or by quarter, you use a totals query to group your records by the desired category and you and so sum the sales figures.
-
Create a crosstab query. A crosstab query is a special blazon of query that displays its results in a filigree that resembles an Excel worksheet. Crosstab queries summarize your values and and then grouping them by ii sets of facts — 1 gear up downwardly the side (row headings), and the other beyond the superlative (column headings). For example, you lot tin can use a crosstab query to display sales totals for each city for the past three years, equally the following tabular array shows:
| City | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 |
| Paris | 254,556 | 372,455 | 467,892 |
| Sydney | 478,021 | 372,987 | 276,399 |
| Jakarta | 572,997 | 684,374 | 792,571 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
Note:The how-to sections in this document emphasize using the Sum function, but think that y'all can apply other aggregate functions in your Total rows and queries. For more information about using the other aggregate functions, see the department Amass office reference later in this article.
For more information almost ways to utilize the other amass functions, meet the article Brandish column totals in a datasheet.
The steps in the following sections explain how to add together a Total row, employ a totals query to sum data across groups, and how to use a crosstab query that subtotals data beyond groups and time intervals. As you proceed, remember that many of the aggregate functions work only on data in fields set to a specific information type. For example, the SUM function works only with fields set to the Number, Decimal, or Currency data types. For more information about the data types that each function requires, see the section Amass function reference, afterwards in this article.
For general information about data types, see the commodity Modify or change the data type set for a field.
Top of Page
Ready some sample information
The how-to sections in this article provide tables of sample data. The how-to steps utilise the sample tables in lodge to aid you understand how the aggregate functions piece of work. If you prefer, you tin can optionally add together the sample tables into a new or existing database.
Access provides several ways to add these sample tables to a database. You lot can enter the information manually, you can copy each table into a spreadsheet program such as Excel and so import the worksheets into Admission, or you tin paste the data into a text editor such as Notepad and import the data from the resulting text files.
The steps in this department explain how to enter information manually in a blank datasheet, and how to re-create the sample tables to a spreadsheet programme, so import those tables into Admission. For more information about creating and importing text data, encounter the article Import or link to information in a text file.
The how-to steps in this article utilise the post-obit tables. Use these tables to create your sample information:
The Categories table:
| Category |
| Dolls |
| Games and Puzzles |
| Art and Framing |
| Video Games |
| DVDs and Movies |
| Models and Hobbies |
| Sports |
The Products table:
| Product Proper noun | Cost | Category |
| Developer action figure | $12.95 | Dolls |
| Fun with C# (A board game for the whole family) | $15.85 | Games and Puzzles |
| Relational Database Diagram | $22.50 | Fine art and Framing |
| The Magical Calculator Fleck (500 Pieces) | $32.65 | Games and Puzzles |
| Admission! The Game! | $22.95 | Games and Puzzles |
| Estimator Geeks and Mythical Creatures | $78.50 | Video Games |
| Exercise for Reckoner Geeks! The DVD! | $14.88 | DVDs and Movies |
| Ultimate Flying Pizza | $36.75 | Sports |
| External 5.25-inch Floppy Diskette Bulldoze (ane/4 Calibration) | $65.00 | Models and Hobbies |
| Bureaucrat non-action figure | $78.88 | Dolls |
| Gloom | $53.33 | Video Games |
| Build Your Own Keyboard | $77.95 | Models and Hobbies |
The Orders table:
| Order Appointment | Ship Engagement | Send City | Shipping Fee |
| 11/xiv/2005 | 11/xv/2005 | Jakarta | $55.00 |
| 11/xiv/2005 | eleven/xv/2005 | Sydney | $76.00 |
| 11/16/2005 | 11/17/2005 | Sydney | $87.00 |
| 11/17/2005 | 11/18/2005 | Dki jakarta | $43.00 |
| 11/17/2005 | xi/18/2005 | Paris | $105.00 |
| 11/17/2005 | 11/18/2005 | Stuttgart | $112.00 |
| 11/18/2005 | 11/xix/2005 | Vienna | $215.00 |
| eleven/nineteen/2005 | 11/xx/2005 | Miami | $525.00 |
| 11/20/2005 | 11/21/2005 | Vienna | $198.00 |
| 11/20/2005 | eleven/21/2005 | Paris | $187.00 |
| 11/21/2005 | 11/22/2005 | Sydney | $81.00 |
| 11/23/2005 | xi/24/2005 | Jakarta | $92.00 |
The Order Details table:
| Society ID | Product Name | Production ID | Unit Cost | Quantity | Discount |
| ane | Build Your Own Keyboard | 12 | $77.95 | 9 | 5% |
| ane | Bureaucrat not-action figure | 2 | $78.88 | 4 | 7.5% |
| 2 | Exercise for Computer Geeks! The DVD! | 7 | $14.88 | 6 | 4% |
| 2 | The Magical Calculator Chip | 4 | $32.65 | 8 | 0 |
| 2 | Computer Geeks and Mythical Creatures | half-dozen | $78.50 | four | 0 |
| three | Access! The Game! | 5 | $22.95 | 5 | 15% |
| 4 | Programmer Action Effigy | 1 | $12.95 | 2 | six% |
| four | Ultimate Flight Pizza | 8 | $36.75 | 8 | iv% |
| v | External 5.25-inch Floppy Diskette Drive (ane/4 Scale) | 9 | $65.00 | 4 | ten% |
| 6 | Relational Database Diagram | 3 | $22.l | 12 | six.v% |
| seven | Gloom | xi | $53.33 | six | 8% |
| seven | Relational Database Diagram | 3 | $22.50 | 4 | ix% |
Annotation:Remember that in a typical database an order details tabular array will contain only a Production ID field, non a Product Name field. The sample table uses a Product Name field to brand the information easier to read.
Enter the sample information manually
-
On the Create tab, in the Tables grouping, click Table.
Access adds a new, bare table to your database.
Note:Y'all do non need to follow this step if you open up a new, blank database, simply you will demand to follow information technology whenever y'all need to add a table to the database.
-
Double-click the outset prison cell in the header row and enter the proper name of the field in the sample table.
By default, Access denotes blank fields in the header row with the text Add New Field, like and then:

-
Use the pointer keys to motion to the next blank header cell , and blazon the 2d field proper name (you can also press TAB or double-click the new cell). Echo this step until yous enter all field names.
-
Enter the information in the sample tabular array.
As you lot enter the data, Access infers a data type for each field. If yous are new to relational databases, you should set a specific data type, such as Number, Text, or Engagement/Fourth dimension, for each of the fields in your tables. Setting the data type helps ensure authentic data entry and also helps preclude mistakes, such as using a phone number in a calculation. For these sample tables, you lot should let Access infer the data blazon.
-
When you finish entering the data, click Save.
Keyboard shortcut Press CTRL+S.
The Save Equally dialog box appears.
-
In the Table Proper noun box, enter the name of the sample tabular array, and then click OK.
You use the name of each sample table because the queries in the how-to sections utilise those names.
-
Echo these steps until you create each of the sample tables listed at the beginning of this section.
If you do not want to enter the information manually, follow the next steps to re-create the information to a spreadsheet file, and so import the data from the spreadsheet file into Access.
Create the sample worksheets
-
Starting time your spreadsheet programme and create a new, blank file. If you apply Excel, information technology creates a new, blank workbook by default.
-
Copy the first sample tabular array provided above and paste it into the first worksheet, starting at the first cell.
-
Using the technique provided by your spreadsheet program, rename the worksheet. Give the worksheet the same name every bit the sample table. For case, if the sample table is named Categories, give your worksheet the same proper name.
-
Echo steps two and three, copying each sample tabular array to a blank worksheet and renaming the worksheet.
Note:Y'all might need to add worksheets to your spreadsheet file. For information on doing that task, run across the help for your spreadsheet program.
-
Save the workbook to a convenient location on your figurer or your network, and get to the next set of steps.
Create database tables from the worksheets
-
On the External Information tab, in the Import group, click Excel.
-or-
Click More than, and and so select a spreadsheet program from the list.
The Get External Data - Program Name Spreadsheet dialog box appears.
-
Click Browse, open the spreadsheet file that you lot created in the previous steps, and then click OK.
The Import Spreadsheet Sorcerer starts.
-
By default, the wizard selects the first worksheet in the workbook (the Customers worksheet, if you followed the steps in the previous section), and data from the worksheet appears in the lower department of the magician page. Click Adjacent.
-
On the next page of the sorcerer, click First row contains column headings, and then click Next.
-
Optionally, on the next page, use the text boxes and lists nether Field Options to change field names and data types or to omit fields from the import performance. Otherwise, click Next.
-
Leave the Permit Access add together principal fundamental choice selected, and click Next.
-
By default, Admission applies the proper name of the worksheet to your new table. Have the name or enter another name, and so click Terminate.
-
Repeats steps 1 through seven until you have created a tabular array from each worksheet in the workbook.
Rename the primary central fields
Annotation:When yous imported the worksheets, Access automatically added a primary cardinal column to each table and, by default, Access named that column "ID" and set it to the AutoNumber information type. The steps in this explain how to rename each primary central field. Doing and then helps to clearly identify all the fields in a query.
-
In the Navigation Pane, right-click each of the tables that y'all created in the previous steps and click Pattern View.
-
For each table, locate the principal key field. By default, Access names each field ID.
-
In the Field Proper noun column for each primary key field, add the proper name of the tabular array.
For case, you would rename the ID field for the Categories table to "Category ID" and the field for the Orders tabular array to "Order ID." For the Order Details table, rename the field to "Detail ID." For the Products tabular array, rename the field to "Product ID."
-
Save your changes.
Whenever the sample tables appear in this commodity, they include the master key field, and the field is renamed equally described by using the preceding steps.
Top of Page
Sum data by using a Total row
You tin can add a Total row to a query by opening your query in Datasheet view, adding the row, and then selecting the aggregate function that you want to use, such every bit Sum, Min, Max, or Avg. The steps in this department explicate how to create a basic select query and add a Total row. You lot do not need to use the sample tables described in the previous section.
Create a basic select query
-
On the Create tab, in the Other group, click Query Design.
-
Double-click the table or tables that you desire to utilize in your query.
The selected table or tables appear as windows in the upper section of the query designer.
-
Double-click the table fields that y'all want to use in your query.
You can include fields that contain descriptive data, such as names and descriptions, but y'all must include a field that contains numeric or currency data.
Each field appears in a cell in the design filigree.
-
Click Run
 to run the query.
to run the query. The query result set up appears in Datasheet view.
-
Optionally, switch to Pattern view and adjust your query. To practice and then, right-click the document tab for the query and click Design View. Yous tin can and then adapt the query, as needed, by adding or removing tabular array fields. To remove a field, select the column in the design grid and press DELETE.
-
Salvage your query.
Add a Full row
-
Make certain that your query is open in Datasheet view. To practise so, right-click the certificate tab for the query and click Datasheet View.
-or-
In the Navigation Pane, double-click the query. This runs the query and loads the results into a datasheet.
-
On the Home tab, in the Records group, click Totals.
A new Total row appears in your datasheet.
-
In the Full row, click the cell in the field that y'all want to sum, and then select Sum from the list.
Hide a Total row
-
On the Home tab, in the Records grouping, click Totals.
For more information about using a Total row, see the commodity Display column totals in a datasheet.
Pinnacle of Page
Calculate grand totals past using a query
A chiliad total is the sum of all the values in a column. You can calculate several types of grand totals, including:
-
A simple grand total that sums the values in a single column. For instance, you can calculate total shipping costs.
-
A calculated grand full that sums the values in more than i cavalcade. For example, you can summate total sales past multiplying the cost of several items by the number of detail ordered, and then totaling the resulting values.
-
A grand total that excludes some records. For example, you tin can calculate the total sales only for terminal Friday.
The steps in the following sections explicate how to create each blazon of grand total. The steps apply the Orders and Order Details tables.
The Orders table
| Club ID | Social club Date | Ship Date | Ship City | Shipping Fee |
| 1 | eleven/14/2005 | 11/15/2005 | Dki jakarta | $55.00 |
| two | eleven/14/2005 | 11/15/2005 | Sydney | $76.00 |
| 3 | 11/sixteen/2005 | 11/17/2005 | Sydney | $87.00 |
| iv | 11/17/2005 | 11/18/2005 | Dki jakarta | $43.00 |
| five | 11/17/2005 | 11/eighteen/2005 | Paris | $105.00 |
| 6 | 11/17/2005 | 11/18/2005 | Stuttgart | $112.00 |
| vii | 11/xviii/2005 | 11/xix/2005 | Vienna | $215.00 |
| 8 | 11/19/2005 | 11/20/2005 | Miami | $525.00 |
| ix | 11/20/2005 | 11/21/2005 | Vienna | $198.00 |
| 10 | xi/20/2005 | xi/21/2005 | Paris | $187.00 |
| 11 | 11/21/2005 | xi/22/2005 | Sydney | $81.00 |
| 12 | eleven/23/2005 | 11/24/2005 | Dki jakarta | $92.00 |
The Order Details tabular array
| Detail ID | Society ID | Production Name | Product ID | Unit Toll | Quantity | Discount |
| 1 | 1 | Build Your Own Keyboard | 12 | $77.95 | 9 | 0.05 |
| 2 | 1 | Bureaucrat non-action figure | 2 | $78.88 | 4 | 0.075 |
| 3 | 2 | Exercise for Computer Geeks! The DVD! | 7 | $xiv.88 | vi | 0.04 |
| iv | 2 | The Magical Computer Scrap | four | $32.65 | eight | 0.00 |
| five | 2 | Computer Geeks and Mythical Creatures | half-dozen | $78.fifty | 4 | 0.00 |
| six | iii | Access! The Game! | 5 | $22.95 | v | 0.15 |
| 7 | iv | Developer Activeness Effigy | 1 | $12.95 | 2 | 0.06 |
| 8 | 4 | Ultimate Flying Pizza | viii | $36.75 | eight | 0.04 |
| 9 | 5 | External five.25-inch Floppy Diskette Drive (i/4 Calibration) | 9 | $65.00 | 4 | 0.10 |
| 10 | 6 | Relational Database Diagram | 3 | $22.50 | 12 | 0.065 |
| 11 | 7 | Gloom | 11 | $53.33 | 6 | 0.08 |
| 12 | seven | Relational Database Diagram | 3 | $22.50 | 4 | 0.09 |
Calculate a simple grand total
-
On the Create tab, in the Other group, click Query Design.
-
Double-click the tabular array that you want to utilize in your query.
If y'all use the sample data, double-click the Orders table.
The tabular array appears in a window in the upper section of the query designer.
-
Double-click the field that you want to sum. Make sure that the field is set to either the Number or Currency information type. If you lot try to sum values in non-numeric fields, such as a Text field, Admission displays the Data type mismatch in criteria expression mistake message when yous try to run the query.
If you use the sample data, double-click the Shipping Fee column.
You can add boosted numeric fields to the filigree if you want to calculate grand totals for those fields. A totals query tin can summate thousand totals for more than one column.
-
On the Design tab, in the Testify/Hibernate group, click Totals.

The Total row appears in the design grid and Group Past appears in the prison cell in the Aircraft Fee column.
-
Change the value in the cell in the Total row to Sum.
-
Click Run
 to run the query and display the results in Datasheet view.
to run the query and display the results in Datasheet view. Tip:Notation that Access appends "SumOf" to the offset of the name of the field that you sum. To alter the column heading to something more meaningful, such as Total Shipping, switch back to Pattern view, and click in the Field row of the Aircraft Fee cavalcade in the pattern grid. Place the cursor next to Shipping Fee and type the words Total Shipping, followed by a colon, like so: Full Shipping: Shipping Fee.
-
Optionally, salve the query and shut it.
Summate a chiliad total that excludes some records
-
On the Create tab, in the Other group, click Query Design.
-
Double-click the Society table and Gild Details table.
-
Add the Order Date field from the Orders table to the first column in the query design filigree.
-
In the Criteria row of the offset column, type Appointment() -one. That expression excludes the electric current day's records from the calculated full.
-
Next, create the column that calculates the sales amount for each transaction. Type the following expression in the Field row of the 2nd column in the grid:
Total Sales Value: (1-[Order Details].[Discount]/100)*([Club Details].[Unit of measurement Price]*[Order Details].[Quantity])
Make sure your expression references fields set up to the Number or Currency data types. If your expression refers to fields set to other data types, Access displays the message Information blazon mismatch in criteria expression when you try to run the query.
-
On the Pattern tab, in the Testify/Hibernate group, click Totals.
The Total row appears in the blueprint grid and Group By appears in the first and second columns.
-
In the second cavalcade, change the value in the prison cell of the Total row to Sum. The Sum part adds the individual sales figures.
-
Click Run
 to run the query and brandish the results in Datasheet view.
to run the query and brandish the results in Datasheet view. -
Salve the query as Daily Sales.
Note:The adjacent time that you open the query in Blueprint view, you might observe a slight modify in the values specified in the Field and Full rows of the Full Sales Value cavalcade. The expression appears enclosed within the Sum function, and the Full row displays Expre ssion instead of Sum.
For example, if you use the sample data and create the query (every bit shown in the previous steps), you see:
Total Sales Value: Sum((1-[Order Details].Disbelieve/100)*([Order Details].Unitprice*[Order Details].Quantity))
Meridian of Page
Calculate group totals by using a totals query
The steps in this section explain how to create a totals query that calculates subtotals across groups of data. As you go along, remember that by default, a totals query can include simply the field or fields that incorporate your group data, such as a "categories" field, and the field that contains the data that you lot want to sum, such as a "sales" field. Totals queries cannot include other fields that depict the items in a category. If you desire to come across that descriptive data, you lot can create a second select query that combines the fields in your totals query with the boosted data fields.
The steps in this section explicate how to create a totals and select queries needed to identify the total sales for each product. The steps assume the use of these sample tables:
The Products table
| Product ID | Product Name | Toll | Category |
| one | Developer action figure | $12.95 | Dolls |
| 2 | Fun with C# (A lath game for the whole family) | $15.85 | Games and Puzzles |
| 3 | Relational Database Diagram | $22.50 | Art and Framing |
| iv | The Magical Figurer Chip (500 Pieces) | $32.65 | Art and Framing |
| 5 | Access! The Game! | $22.95 | Games and Puzzles |
| vi | Reckoner Geeks and Mythical Creatures | $78.50 | Video Games |
| 7 | Exercise for Computer Geeks! The DVD! | $14.88 | DVDs and Movies |
| 8 | Ultimate Flying Pizza | $36.75 | Sports |
| ix | External 5.25-inch Floppy Diskette Bulldoze (1/4 Scale) | $65.00 | Models and Hobby |
| 10 | Bureaucrat non-action effigy | $78.88 | Dolls |
| xi | Gloom | $53.33 | Video Games |
| 12 | Build Your Own Keyboard | $77.95 | Models and Hobby |
The Society Details tabular array
| Detail ID | Club ID | Product Name | Product ID | Unit Price | Quantity | Disbelieve |
| 1 | one | Build Your Own Keyboard | 12 | $77.95 | 9 | 5% |
| 2 | ane | Bureaucrat non-action figure | two | $78.88 | 4 | 7.5% |
| 3 | 2 | Practise for Computer Geeks! The DVD! | seven | $14.88 | 6 | four% |
| 4 | 2 | The Magical Computer Scrap | 4 | $32.65 | eight | 0 |
| 5 | 2 | Reckoner Geeks and Mythical Creatures | six | $78.l | iv | 0 |
| 6 | three | Access! The Game! | v | $22.95 | 5 | 15% |
| 7 | four | Programmer Action Effigy | 1 | $12.95 | 2 | 6% |
| 8 | 4 | Ultimate Flying Pizza | eight | $36.75 | 8 | four% |
| 9 | 5 | External 5.25-inch Floppy Diskette Drive (ane/4 Scale) | 9 | $65.00 | 4 | x% |
| 10 | 6 | Relational Database Diagram | 3 | $22.fifty | 12 | 6.5% |
| 11 | 7 | Gloom | xi | $53.33 | 6 | eight% |
| 12 | 7 | Relational Database Diagram | iii | $22.50 | 4 | ix% |
The following steps assume a one-to-many human relationship between the Production ID fields in the Orders tabular array and Lodge Details table, with the Orders table on the "one" side of the human relationship.
Create the totals query
-
On the Create tab, in the Other grouping, click Query Blueprint.
-
Select the tables that you want to work with, so click Add.
Each table appears every bit a window in the upper section of the query designer.
If you lot use the sample tables listed previously, you add together the Products and Order Details tables.
-
Double-click the table fields that you want to apply in your query.
Equally a rule, y'all add but the grouping field and the value field to the query. However, you tin can use a calculation instead of a value field — the next steps explicate how to do so.
-
Add the Category field from the Products table to the blueprint filigree.
-
Create the column that calculates the sales amount for each transaction by typing the following expression in the second column in the filigree:
Total Sales Value: (1-[Order Details].[Discount]/100)*([Order Details].[Unit Price]*[Guild Details].[Quantity])
Make certain that the fields that you reference in the expression are of the Number or Currency data types. If y'all reference fields of other data types, Admission displays the fault bulletin Data blazon mismatch in criteria expression when you try to switch to Datasheet view.
-
On the Blueprint tab, in the Show/Hibernate group, click Totals.
The Total row appears in the pattern grid, and in that row, Group Past appears in the first and 2d columns.
-
In the second column, alter the value in the Total row to Sum. The Sum function adds the individual sales figures.
-
Click Run
 to run the query and display the results in Datasheet view.
to run the query and display the results in Datasheet view. -
Keep the query open for use in the side by side section.
Apply criteria with a totals query
The query that yous created in the previous section includes all the records in the underlying tables. Information technology does not exclude whatever gild when calculating the totals, and it displays the totals for all categories.
If you need to exclude some records, you lot can add together criteria to the query. For example, you tin ignore transactions that are less than $100 or calculate totals for only some of your product categories. The steps in this section explain how to use three types of criteria:
-
Criteria that ignore sure groups when calculating totals. For instance, yous will calculate totals for just the Video Games, Art and Framing, and Sports categories.
-
Criteria that hide sure totals after calculating them. For instance, yous can display merely the totals greater than $150,000.
-
Criteria that exclude individual records from beingness included in the total. For example, y'all tin can exclude individual sales transactions when the value (Unit Price * Quantity) drops below $100.
The following steps explain how to add the criteria one by one and see the impact on the query consequence.
Add together criteria to the query
-
Open the query from the previous section in Pattern view. To exercise so, right-click the document tab for the query and click Design View.
-or-
In the Navigation Pane, right-click the query and click Design View.
-
In the Criteria row of the Category ID cavalcade, type =Dolls Or Sports or Art and Framing.
-
Click Run
 to run the query and display the results in Datasheet view.
to run the query and display the results in Datasheet view. -
Switch back to Design view and, in the Criteria row of the Total Sales Value column, type >100.
-
Run the query to run into the results, and so switch back to Design view.
-
Now add the criteria to exclude individual sales transactions that are less than $100. To do this, you need to add some other column.
Annotation:You lot cannot specify the third criteria in the Total Sales Value column. Any criteria that you specify in this column applies to the total value, non to the individual values.
-
Copy the expression from the second column to the 3rd column.
-
In the Total row for the new column, select Where and, in the Criteria row, blazon >20.
-
Run the query to see the results, and and so relieve the query.
Note:The adjacent time you open up the query in Blueprint view, you might notice slight changes in the pattern grid. In the second column, the expression in the Field row will appear enclosed within the Sum function, and the value in the Total row displays Expression instead of Sum.
Total Sales Value: Sum((1-[Order Details].Discount/100)*([Club Details].Unitprice*[Orde r Details].Quantity))
You will also see a quaternary column. This column is a copy of the 2d column, but the criteria that you specified in the second column really appears as office of the new cavalcade.
-
Top of Folio
Sum data across multiple groups by using a crosstab query
A crosstab query is a special type of query that displays its results in a grid similar to an Excel worksheet. Crosstab queries summarize your values and then group them by ii sets of facts — one set down the side (a gear up of row headers), and the other across the top (a set of cavalcade headers). This figure illustrates part of the event set for sample crosstab query:
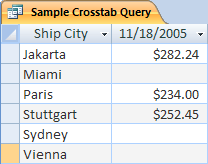
As y'all go on, remember that a crosstab query does not e'er populate all the fields in the effect fix because the tables that yous employ in the query do not always comprise values for every possible data point.
When you create a crosstab query, yous typically include information from more 1 table, and you always include three types of information: the data used as row headings, the data used as column headings, and the values that you lot desire to sum or otherwise compute.
The steps in this section assume the following tables:
The Orders table
| Order Date | Send Date | Ship City | Shipping Fee |
| 11/fourteen/2005 | 11/15/2005 | Dki jakarta | $55.00 |
| 11/14/2005 | 11/15/2005 | Sydney | $76.00 |
| 11/xvi/2005 | eleven/17/2005 | Sydney | $87.00 |
| eleven/17/2005 | 11/eighteen/2005 | Jakarta | $43.00 |
| xi/17/2005 | xi/18/2005 | Paris | $105.00 |
| xi/17/2005 | 11/18/2005 | Stuttgart | $112.00 |
| eleven/eighteen/2005 | xi/19/2005 | Vienna | $215.00 |
| xi/19/2005 | eleven/20/2005 | Miami | $525.00 |
| 11/20/2005 | 11/21/2005 | Vienna | $198.00 |
| eleven/xx/2005 | eleven/21/2005 | Paris | $187.00 |
| 11/21/2005 | 11/22/2005 | Sydney | $81.00 |
| 11/23/2005 | eleven/24/2005 | Jakarta | $92.00 |
The Order Details table
| Order ID | Product Proper noun | Product ID | Unit Price | Quantity | Discount |
| 1 | Build Your Own Keyboard | 12 | $77.95 | 9 | 5% |
| ane | Bureaucrat non-activeness figure | ii | $78.88 | four | 7.5% |
| 2 | Exercise for Computer Geeks! The DVD! | 7 | $14.88 | 6 | 4% |
| 2 | The Magical Estimator Chip | 4 | $32.65 | eight | 0 |
| 2 | Computer Geeks and Mythical Creatures | 6 | $78.fifty | iv | 0 |
| 3 | Access! The Game! | 5 | $22.95 | 5 | 15% |
| iv | Programmer Action Figure | 1 | $12.95 | 2 | half dozen% |
| 4 | Ultimate Flying Pizza | 8 | $36.75 | 8 | 4% |
| 5 | External 5.25-inch Floppy Diskette Drive (1/4 Calibration) | ix | $65.00 | 4 | 10% |
| 6 | Relational Database Diagram | iii | $22.50 | 12 | 6.five% |
| 7 | Gloom | 11 | $53.33 | half dozen | eight% |
| 7 | Relational Database Diagram | 3 | $22.l | iv | 9% |
The following steps explain how to create a crosstab query that groups total sales by city. The query uses two expressions to return a formatted date and a sales total.
Create a crosstab query
-
On the Create tab, in the Other group, click Query Design.
-
Double-click the tables that you want to employ in your query.
Each table appears as a window in the upper section of the query designer.
If you use the sample tables, double-click the Orders table and the Guild Details table.
-
Double-click the fields that yous want to utilize in your query.
Each field name appears in the a blank cell in the Field row of the design filigree.
If yous use the sample tables, add the Transport Metropolis and Ship Date fields from the Orders table.
-
In the side by side blank cell in the Field row, copy and paste or type the following expression: Total Sales: Sum(CCur([Order Details].[Unit Price]*[Quantity]*(i-[Discount])/100)*100)
-
On the Design tab, in the Query Type group, click Crosstab.
The Full row and the Crosstab row announced in the design grid.
-
Click the cell in the Total row in the City field and select Group By. Exercise the same for the Ship Date field. Change the value in the Full prison cell of the Full Sales field to Expression.
-
In the Crosstab row, fix the cell in the Urban center field to Row Heading, set the Transport Date field to Cavalcade Heading, and set the Total Sales field to Value.
-
On the Blueprint tab, in the Results group, click Run.
The query results appear in Datasheet view.
Top of Page
Amass office reference
This tabular array lists and describes the aggregate functions that Access provides in the Total row and in queries. Call up that Access provides more than aggregate functions for queries than information technology does for the Total row. Also, if yous work with an Access project (an Access front finish connected to a Microsoft SQL Server database), you tin can utilize the larger prepare of aggregate functions that SQL Server provides. For more information about that set up of functions, see Microsoft SQL Server Books Online.
| Role | Description | Us e with the information blazon(southward) |
| Average | Calculates the boilerplate value for a cavalcade. The column must contain numeric, currency, or appointment/fourth dimension information. The function ignores cipher values. | Number, Currency, Engagement/Time |
| Count | Counts the number of items in a cavalcade. | All information types except complex repeating scalar data, such as a column of multivalued lists. For more than information about multivalued lists, see the articles Guide to multivalued fields and Create or delete a multivalued field. |
| Maximum | Returns the particular with the highest value. For text data, the highest value is the concluding alphabetic value — Access ignores example. The function ignores zippo values. | Number, Currency, Date/Time |
| Minimum | Returns the item with the lowest value. For text data, the lowest value is the starting time alphabetic value — Admission ignores case. The role ignores zippo values. | Number, Currency, Date/Time |
| Standard Divergence | Measures how widely values are dispersed from an average value (a hateful). For more than information almost using this function, see the article Display column totals in a datasheet. | Number, Currency |
| Sum | Adds the items in a column. Works just on numeric and currency data. | Number, Currency |
| Variance | Measures the statistical variance of all values in the cavalcade. You can use this function merely on numeric and currency data. If the table contains less than 2 rows, Access returns a null value. For more information virtually variance functions, come across the commodity Display column totals in a datasheet. | Number, Currency |
Top of Folio
How To Sum A Variable By Group In Network Data R,
Source: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/sum-data-by-using-a-query-430a669b-e7fd-4c4b-b154-8c8dbbe41c8a
Posted by: monarrezyousses.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Sum A Variable By Group In Network Data R"
Post a Comment