What Is Big Data And What Are Its Beneã¯â¬âts?
What is big information?
Big data is a combination of structured, semistructured and unstructured data collected past organizations that tin can be mined for information and used in car learning projects, predictive modeling and other advanced analytics applications.
Systems that process and store big data take become a mutual component of data direction architectures in organizations, combined with tools that support big data analytics uses. Big data is oftentimes characterized by the three V'southward:
- the large book of data in many environments;
- the wide variety of data types frequently stored in big information systems; and
- the velocity at which much of the information is generated, collected and candy.
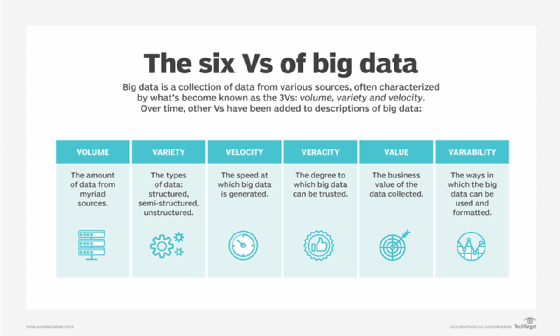
These characteristics were first identified in 2001 by Doug Laney, then an analyst at consulting house Meta Grouping Inc.; Gartner further popularized them subsequently it acquired Meta Group in 2005. More recently, several other Five's have been added to different descriptions of big data, including veracity, value and variability.
Although large data doesn't equate to any specific volume of data, big data deployments oft involve terabytes, petabytes and even exabytes of information created and collected over time.
Why is big information of import?
Companies use big information in their systems to improve operations, provide improve customer service, create personalized marketing campaigns and take other actions that, ultimately, can increase revenue and profits. Businesses that use it effectively hold a potential competitive reward over those that don't because they're able to make faster and more than informed business decisions.
For example, big data provides valuable insights into customers that companies can employ to refine their marketing, advertising and promotions in social club to increment customer engagement and conversion rates. Both historical and real-time data can be analyzed to assess the evolving preferences of consumers or corporate buyers, enabling businesses to become more responsive to customer wants and needs.
Large information is also used by medical researchers to identify disease signs and hazard factors and by doctors to assistance diagnose illnesses and medical conditions in patients. In addition, a combination of data from electronic health records, social media sites, the web and other sources gives healthcare organizations and government agencies up-to-date data on infectious illness threats or outbreaks.
Here are some more than examples of how big data is used by organizations:
- In the energy industry, large data helps oil and gas companies identify potential drilling locations and monitor pipeline operations; as well, utilities use information technology to rails electrical grids.
- Financial services firms use big data systems for risk management and real-fourth dimension analysis of market information.
- Manufacturers and transportation companies rely on large information to manage their supply chains and optimize delivery routes.
- Other regime uses include emergency response, crime prevention and smart city initiatives.

What are examples of large data?
Big data comes from myriad sources -- some examples are transaction processing systems, customer databases, documents, emails, medical records, internet clickstream logs, mobile apps and social networks. It also includes car-generated data, such equally network and server log files and information from sensors on manufacturing machines, industrial equipment and internet of things devices.
In addition to information from internal systems, big information environments oftentimes incorporate external data on consumers, financial markets, weather and traffic atmospheric condition, geographic information, scientific research and more. Images, videos and sound files are forms of big data, too, and many large information applications involve streaming information that is processed and collected on a continual basis.
Breaking downwardly the V's of big information
Book is the almost ordinarily cited characteristic of big data. A big information environment doesn't have to incorporate a large amount of information, simply most do because of the nature of the information existence collected and stored in them. Clickstreams, system logs and stream processing systems are among the sources that typically produce massive volumes of data on an ongoing footing.
Big data too encompasses a broad variety of information types, including the following:
- structured data, such as transactions and financial records;
- unstructured data, such as text, documents and multimedia files; and
- semistructured data, such every bit spider web server logs and streaming data from sensors.
Diverse data types may need to be stored and managed together in large data systems. In add-on, large data applications oft include multiple data sets that may not be integrated upfront. For instance, a big information analytics project may attempt to forecast sales of a product by correlating data on by sales, returns, online reviews and client service calls.
Velocity refers to the speed at which data is generated and must be processed and analyzed. In many cases, sets of large data are updated on a real- or well-nigh-real-time footing, instead of the daily, weekly or monthly updates made in many traditional data warehouses. Managing data velocity is besides important equally big information analysis further expands into machine learning and bogus intelligence (AI), where analytical processes automatically find patterns in data and employ them to generate insights.
More characteristics of big data
Looking beyond the original iii V's, here are details on some of the other ones that are at present ofttimes associated with big data:
- Veracity refers to the degree of accuracy in data sets and how trustworthy they are. Raw data collected from various sources tin cause data quality issues that may exist difficult to pinpoint. If they aren't fixed through data cleansing processes, bad data leads to analysis errors that can undermine the value of business analytics initiatives. Data management and analytics teams also need to ensure that they accept enough accurate information bachelor to produce valid results.
- Some data scientists and consultants besides add together value to the list of big information's characteristics. Not all the data that's collected has existent business organization value or benefits. As a event, organizations need to confirm that data relates to relevant concern problems before it's used in big information analytics projects.
- Variability as well often applies to sets of big data, which may accept multiple meanings or be formatted differently in split up data sources -- factors that further complicate large data management and analytics.
Some people ascribe fifty-fifty more V'south to large data; various lists accept been created with betwixt seven and 10.
How is big data stored and processed?
Big data is frequently stored in a data lake. While data warehouses are ordinarily congenital on relational databases and contain structured data only, information lakes can back up various data types and typically are based on Hadoop clusters, deject object storage services, NoSQL databases or other big data platforms.
Many large information environments combine multiple systems in a distributed architecture; for instance, a central data lake might be integrated with other platforms, including relational databases or a data warehouse. The data in big information systems may be left in its raw course and then filtered and organized as needed for item analytics uses. In other cases, information technology'south preprocessed using information mining tools and data preparation software so it's gear up for applications that are run regularly.
Large data processing places heavy demands on the underlying compute infrastructure. The required computing power often is provided past clustered systems that distribute processing workloads across hundreds or thousands of article servers, using technologies similar Hadoop and the Spark processing engine.
Getting that kind of processing capacity in a cost-effective way is a challenge. As a result, the cloud is a pop location for big data systems. Organizations can deploy their own cloud-based systems or use managed big-data-as-a-service offerings from cloud providers. Deject users can calibration upward the required number of servers just long plenty to complete big information analytics projects. The business organization only pays for the storage and compute time information technology uses, and the cloud instances tin be turned off until they're needed again.
How big data analytics works
To get valid and relevant results from big data analytics applications, data scientists and other information analysts must accept a detailed understanding of the available data and a sense of what they're looking for in it. That makes data preparation, which includes profiling, cleansing, validation and transformation of data sets, a crucial start footstep in the analytics process.
Once the data has been gathered and prepared for analysis, various information science and avant-garde analytics disciplines tin can be applied to run different applications, using tools that provide large data analytics features and capabilities. Those disciplines include machine learning and its deep learning offshoot, predictive modeling, data mining, statistical assay, streaming analytics, text mining and more than.
Using customer data as an example, the different branches of analytics that tin be washed with sets of large data include the post-obit:
- Comparative analysis. This examines customer behavior metrics and real-fourth dimension client engagement in club to compare a company's products, services and branding with those of its competitors.
- Social media listening . This analyzes what people are saying on social media about a concern or product, which tin can help identify potential problems and target audiences for marketing campaigns.
- Marketing analytics . This provides information that can be used to amend marketing campaigns and promotional offers for products, services and business initiatives.
- Sentiment analysis. All of the data that's gathered on customers can be analyzed to reveal how they feel virtually a company or brand, client satisfaction levels, potential problems and how customer service could be improved.
Big data direction technologies
Hadoop, an open up source distributed processing framework released in 2006, initially was at the center of most big data architectures. The development of Spark and other processing engines pushed MapReduce, the engine congenital into Hadoop, more to the side. The result is an ecosystem of large information technologies that tin be used for different applications but oftentimes are deployed together.
Big information platforms and managed services offered by IT vendors combine many of those technologies in a single package, primarily for use in the cloud. Currently, that includes these offerings, listed alphabetically:
- Amazon EMR (formerly Elastic MapReduce)
- Cloudera Data Platform
- Google Cloud Dataproc
- HPE Ezmeral Information Fabric (formerly MapR Data Platform)
- Microsoft Azure HDInsight
For organizations that want to deploy big information systems themselves, either on bounds or in the cloud, the technologies that are available to them in addition to Hadoop and Spark include the following categories of tools:
- storage repositories, such as the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and cloud object storage services that include Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), Google Cloud Storage and Azure Hulk Storage;
- cluster management frameworks, like Kubernetes, Mesos and YARN, Hadoop's built-in resources manager and job scheduler, which stands for Notwithstanding Another Resources Negotiator but is unremarkably known by the acronym lonely;
- stream processing engines, such as Flink, Hudi, Kafka, Samza, Storm and the Spark Streaming and Structured Streaming modules built into Spark;
- NoSQL databases that include Cassandra, Couchbase, CouchDB, HBase, MarkLogic Information Hub, MongoDB, Neo4j, Redis and various other technologies;
- data lake and data warehouse platforms, amid them Amazon Redshift, Delta Lake, Google BigQuery, Kylin and Snowflake; and
- SQL query engines, similar Drill, Hive, Impala, Presto and Trino.
Large data challenges
In connection with the processing capacity bug, designing a big data architecture is a mutual challenge for users. Big information systems must be tailored to an organization's particular needs, a DIY undertaking that requires IT and data management teams to slice together a customized prepare of technologies and tools. Deploying and managing big data systems also crave new skills compared to the ones that database administrators and developers focused on relational software typically possess.
Both of those issues can be eased by using a managed deject service, merely It managers demand to keep a shut eye on cloud usage to make sure costs don't become out of manus. Also, migrating on-premises data sets and processing workloads to the cloud is often a circuitous process.
Other challenges in managing large information systems include making the data accessible to data scientists and analysts, especially in distributed environments that include a mix of different platforms and data stores. To help analysts find relevant data, data management and analytics teams are increasingly building information catalogs that comprise metadata management and data lineage functions. The process of integrating sets of big data is often also complicated, specially when data variety and velocity are factors.
Keys to an constructive big data strategy
In an organization, developing a large data strategy requires an understanding of business organisation goals and the data that'due south currently available to use, plus an assessment of the need for additional data to help meet the objectives. The next steps to take include the following:
- prioritizing planned utilise cases and applications;
- identifying new systems and tools that are needed;
- creating a deployment roadmap; and
- evaluating internal skills to see if retraining or hiring are required.
To ensure that sets of big data are make clean, consequent and used properly, a data governance program and associated information quality management processes also must be priorities. Other best practices for managing and analyzing big data include focusing on business organization needs for information over the available technologies and using information visualization to help in information discovery and assay.
Big data collection practices and regulations
As the collection and use of big information have increased, and then has the potential for data misuse. A public outcry nigh data breaches and other personal privacy violations led the European union to approve the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), a data privacy constabulary that took effect in May 2018. GDPR limits the types of data that organizations can collect and requires opt-in consent from individuals or compliance with other specified reasons for collecting personal information. It as well includes a right-to-be-forgotten provision, which lets EU residents ask companies to delete their data.
While there aren't like federal laws in the U.S., the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) aims to give California residents more control over the collection and use of their personal information by companies that exercise business in the state. CCPA was signed into law in 2018 and took outcome on January. 1, 2020.
To ensure that they comply with such laws, businesses need to advisedly manage the procedure of collecting big data. Controls must be put in place to place regulated data and prevent unauthorized employees from accessing it.
The human side of big information management and analytics
Ultimately, the business value and benefits of big information initiatives depend on the workers tasked with managing and analyzing the data. Some large data tools enable less technical users to run predictive analytics applications or help businesses deploy a suitable infrastructure for large data projects, while minimizing the need for hardware and distributed software know-how.
Big data can be contrasted with small data, a term that's sometimes used to describe information sets that can be easily used for self-service BI and analytics. A commonly quoted precept is, "Big data is for machines; small data is for people."
What Is Big Data And What Are Its Beneã¯â¬âts?,
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchdatamanagement/definition/big-data
Posted by: monarrezyousses.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is Big Data And What Are Its Beneã¯â¬âts?"
Post a Comment